Semiconductor
Electrical conduction in solids : The conduction of electron (charge) depends on various factor such as availability of free electrons, crystalline structure, temperature, nature of defects present in the solid, charge carriers, etc. Based on this factor we can classify material into three category viz. a) conductor b) semiconductor c) Insulator. Let us study all this three category.
Conductors : The material having large number of conduction electron (Free electron) is capable of conducting electric current. The metals are sea of free electron. The free electron is responsible for electric current. Thus metal is a good conductor of electricity.In normal metal there are approximately 1028 electrons in m3 .Eg : Copper , aluminium, iron,etc.
Insulator : The material having very less number of conduction electron (Free electron) is not capable of conducting electric current. The non - metals mostly have valence electron and not free electron. The free electron is responsible for electric current. Thus non-metal is bad conductor of electricity.In normal non-metal there are approximately 1023electrons in m3 .Eg : Plastic, Rubber, Glass,etc.
Semiconductor : Semiconductor is a device whose conductivity lie between conductivity of Conductor and Insulator. In certain condition it is possible to use it as a conductor as well as insulator. The conductivity of semiconductor lies between 104 to 10-6 Sm-1 .The conductivity vary from one semiconductor to another semiconductor depending upon atomic bonding and availability of free electrons.
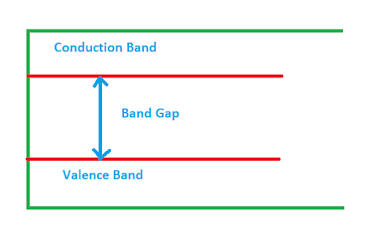
The number of charge carrier can be controlled by varying temperature.The behaviour of semiconductor can be studied by understanding band theory.Silicon, germanium,
gallium arsenide, gallium nitride, cadmium
sulphide are some of the commonly used
semiconductors.
 |
| Photo by Christian Wiediger on Unsplash |









No comments:
Post a Comment