Magnetism
Introduction : Concept of magnet was studied by many scientist like William Gilbert (1544-
1603), Danish physicist Hans Oersted (1777-
1851), James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) . But the applications of magnet has been develop in late 19th century which had led the industrial revolution a step ahead. In lower classes we have learned about magnet and general behaviour of a magnet i.e when same poles of a magnet are brought together they repel each other and when unlike poles are brought together they attract each other. Let us under the properties of magnet in detais in this topic.
Try this interesting experiment by your own
Loading please wait........
Concept related to magnet
1) When a magnet is freely suspended using a string, it comes to rest in geographical north south direction.
2) Two poles of the magnet cannot be sepearted from each other.
3)The magnetic strength is always located at the pole.
4)Every magnet has a two poles i.e north and south pole.
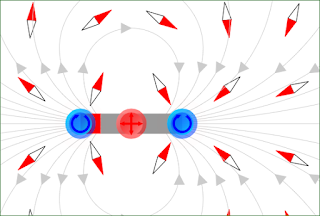
PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC FEILD LINES :
1) Magnetic field lines always originate from north pole and terminates at south poles. Inside a magnet the field lines is from south to north pole. It always form a closed loop.
2)The direction of the net magnetic field 'B' at a point is given by the tangent to the
magnetic line of force at that point in the
direction of line of force.
3) The number of magnetic field line per unit area gives the magnitude of magnetic field.
4)No magnetic field lines can intersect with each other.
Parameter related to magnetic field :
The strength of a magnetic field is expressed in terms of vector quantity called as magnetic induction (Magnetic field) B.
Magnetic field (B) at a given point is defined as magnetic flux per unit area.
Mathematically,
B = ф/ A
SI unit is Tesla or weber/m2
Magnetic flux (ф) number of magnetic field lines passing normally through a given area.
Mathematically,
ф= B.A
SI unit is Weber
Concept of a bar magnet
 |
| Bar magnet |
Axis : It is the line passing through both the poles of the magnet.
Equator : A line passing through centre of a magnet and perpendicular to the axis is called as equator.
Magnetic Length(2l) : The distance between two poles of the magnet is called as magnetic length.








Thank u 😊 sir
ReplyDelete👍👍👍
ReplyDelete