Structure of atoms and nuclei
Introduction: In an earlier century around 300 - 400 BC, many philosophers(Leucippus, Democritus) suggested that every object in the universe is made up of very tiny particles called atoms. In 600 BC an Indian scholar and philosopher, Maharishi kannad gave the first conceptualized idea about the matter. He explained that every matter is made up of a very tiny indestructive particle (anu) atom. These tiny particles pervade the universe and do not change their form in any situation. Later this theory was further developed by many other scientists in the late 17th century. In this topic, we shall discuss the concept of the atom in detail.
Dalton atomic model :
 |
| Dalton atomic model |
1) He stated that every matter is made up of a tiny particle called an atom.
2) This particle is indestructible.
3) Atoms of a given element are similar in structure and physical properties.
4) When these atoms combine, we get a different substance.
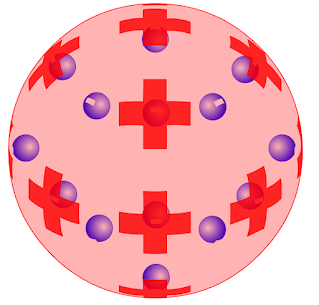
JJ Thomson atomic model: JJ Thomson performed several vacuum tube experiments with different gases and concluded that on applying an electric field this system emits rays which was containing a negative charge.Thus he discovered negatively charged electrons in an atom.
 |
| JJ Thomson Atomic Model |
1) Atoms are positively charged systems having negatively charged particle 'electrons' embedded inside them.
2)The number of positive charges and negative charges in an atom is equal which makes an atom electrically neutral.
3) The positive charge from an atom cannot come out but a negatively charged electron can come about by supplying extra energy to an atom.
4) This model was similar to a watermelon where the red part represents the positively charged atom and the seed represent embedded electrons.
5) This model was referred to as the Plum-pudding model.
Further study was made to study the structure of the atom but it did not support the theory proposed by JJ Thomson. In 1911 Ernst Rutherford gave his atomic model by suggesting a gold foil experiment which was performed by Geiger and Marsden.
Related Topics: Atomic Structure Geiger and Marsden Experiment Atomic Spectra Bohr's Postulate Radius of an orbit Velocity of an electron Energy of an orbit Limitation of Bohr's Model De Broglie's explanation Atomic Nucleus Nuclear Binding energy Radioactivity Laws of radioactivity Nuclear energy







No comments:
Post a Comment