Geiger and Marsden Experiment setup
In order to understand the atomic structure, Rutherford came up with an experiment that was performed by Geiger and Marsden. Here is an experimental setup of the experiment
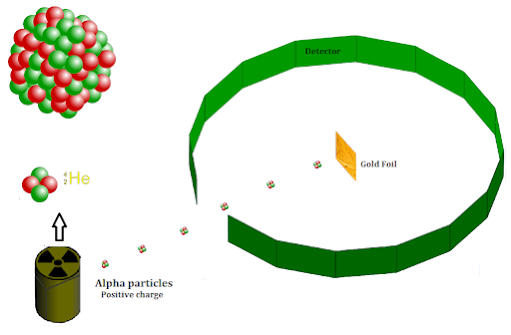 |
| Geiger and Marsden Experiment setup |
Observation obtained from the experiments
1) Large number of alpha particles passed straight through the foil without any deviation.
2) Very few particles approximately 0.14% deviated through an angle greater than 0.10
3) 1 particle out of 8000 was deflected at an angle greater than 9004) Very few reflected back at 1800
This experiment was unable to explain JJ Thomson's atomic model. Thus rutherford came up with his conclusion. He explained that if most of the particles passed without any deviation, this signifies that the atom is almost an empty space. Rutherford argued with the observation that why few particles returned back straight? This concludes that alpha particles must have encountered a massive mass of positively charged particles. Thus from the experimental observation, he obtained the following conclusion:
Rutherford Conclusion
1) Atom is 99.9% empty space.
2) Very little space 0.1% is occupied by a positive charge which he called a nucleus.
3) Almost all the mass of an atom is concentrated at the center.
4) Electrons revolve around the atom in a circular orbit similar to the solar system.
5) These electrons are held in the orbit due to the electrostatic force of attraction between electron and nucleus
Rutherford Atomic Model
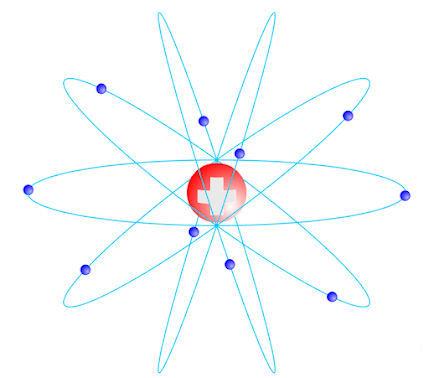 |
| Rutherford atomic Model |
Related Topics: Atomic Structure Geiger and Marsden Experiment Atomic Spectra Bohr's Postulate Radius of an orbit Velocity of an electron Energy of an orbit Limitation of Bohr's Model De Broglie's explanation Atomic Nucleus Nuclear Binding energy Radioactivity Laws of radioactivity Nuclear energy







No comments:
Post a Comment