Bohr's Postulate
Introduction: There were some difficulties in rutherford's atomic model. This model could not properly explain the motion of the electron around the nucleus (accelerated motion). Bohr came up with his postulate to overcome this difficulty. He was able to solve this difficulty using quantum physics. Let us understand it in detail.
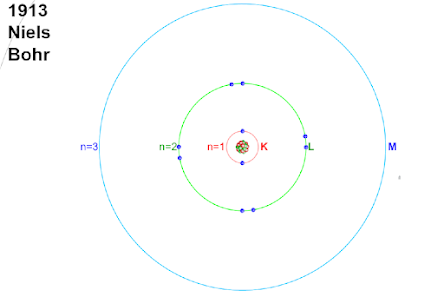
Bohr's First Postulate: Every electron revolves around the atom in a fixed stable orbit without radiating any energy.
Mathematically,
The electron is held in the orbit due to the electrostatic force between the electron and nucleus. This electrostatic force balance centripetal force during the revolution.
Centripetal force = Electrostatic force
Bohr's Second Postulate: Every electron revolves around the atom in an orbit where the angular momentum of the electron is equal to an integral multiple of h / 2π
Mathematically,
Angular momentum = n * h/2π
Bohr's Third Postulate: During the transition from a higher orbit to a lower orbit, electron radiated energy in the form of an electromagnetic wave having energy equal to the difference in energy of both the orbit.
Mathematically,










No comments:
Post a Comment