Angle of Contact
Introduction: have you seen surface of the water in a glass? the surface is having concave surface. Whenever a liquid is placed in a container , the surface of the liquid may be concave or convex. The shape of the surface is determined by a important parameter called as Angle of contact. We will study this topic in detail in this section.
 |
| Fig1. Angle of contact |
Angle of contact : Angle between the tangent drawn on solid and liquid surface in contact is called as Angle of contact.
Figure shows angle of contact between liquid and solid interface.
Shape of a meniscus
1) Concave meniscus : The shape of the meniscus depends upon the direction of resultant force in the system which is in contact. The fig2 below shows concave meniscus.
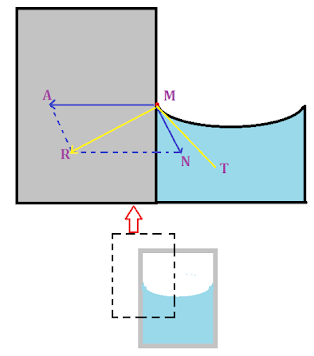 |
| Figure 2. Concave meniscus |
Consider a molecule M on the surface of the liquid which is in contact with container. There exist a adhesive force on the molecule due to solid surface. This adhesive force AM acting on the molecule is perpendicular to the surface since the surface is vertical and acts towards the solid. The cohesive force MN which is at an angle of 45० with both liquid and solid surface acts toward liquid. The adhesive force is much larger than the cohesive force, thus according to parallelogram law of vector addition the resultant force MR is towards solid. For equilibrium, the surface of the liquid or tangent MT must be perpendicular to the resultant force. Thus the surface near the contact moves up in order to adjust itself perpendicular to the resultant force. Hence the surface looks concave.
2) Convex meniscus : The shape of the meniscus depends upon the direction of resultant force in the system which is in contact. The fig3 below shows convex meniscus.
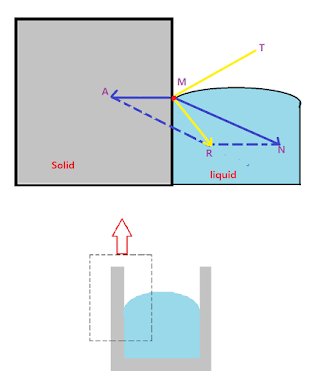 |
| Figure 3. Convex meniscus |
Join our telegram channel for more updates and notes
<<<https://t.me/physicspadhai>>>
Join our instagram channel for more updates and notes
3)Zero angle of contact : The shape of the meniscus depends upon the direction of resultant force in the system which is in contact. The fig4 below shows zero angle of contact.
 |
| Figure 4. zero angle of contact |
4)Angle of contact 90० : The shape of the meniscus depends upon the direction of resultant force in the system which is in contact. The fig5 below shows angle of contact 90० .
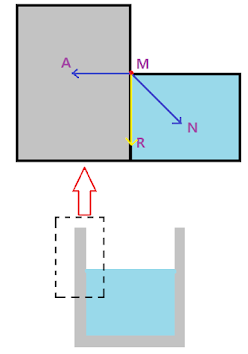 |
| Fig5. Angle of contact 90० |
Consider a molecule M on the surface of the liquid (hypothetical) which is in contact with container. Consider a molecule M on the surface of the liquid which is in contact with container. There exist a adhesive force on the molecule due to solid surface. This adhesive force AM acting on the molecule is perpendicular to the surface since the surface is vertical and acts towards the solid. The cohesive force MN which is at an angle of 45० with both liquid and solid surface acts toward liquid, thus the resultant force MR is exactly vertically . For equilibrium, the surface of the liquid must be perpendicular to the resultant force. Thus the surface near the contact adjust itself perpendicular to the resultant force. Hence the surface looks plane.
Condition for concavity and convexity
Below fig is a part of fig 5 above,

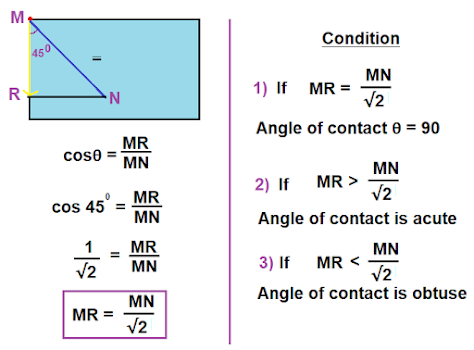






No comments:
Post a Comment